Natural sitelinks seem beneath an inventory in search outcomes. Google offers no clear pointers on optimizing for sitelinks, making them unpredictable.
Right here’s what we all know and suspect.
Natural Sitelinks
Natural sitelinks seem in two varieties:
- Branded.
- “Mini” (a single line).
Branded sitelinks present for brand-name search queries and are all the time on the high. Google inserts branded sitelinks in largely excessive authority websites for recognized “entities,” high-volume queries Google is aware of as manufacturers.
Typically branded sitelinks embody a field to go looking the location proper from Google. Google’s tutorial addresses how you can use structured information to extend the possibilities of a sitelink search field.
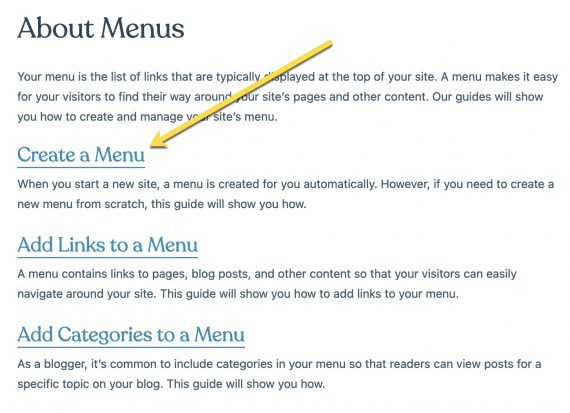
Most often, nonetheless, branded sitelinks are from the primary navigation, corresponding to this instance for an “ebay” question.
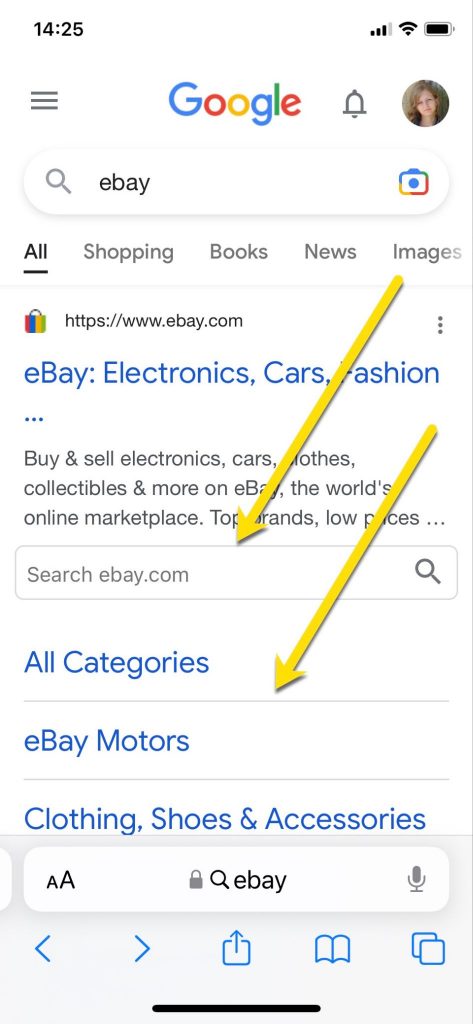
Branded sitelinks are normally from the primary navigation, corresponding to this instance for an “ebay” question.
Mini sitelinks largely present up within the high 10 natural outcomes. Mini sitelinks are contextual — i.e., based mostly on the search question.

Mini sitelinks are contextual, corresponding to for this question “how you can copy twitter profile hyperlink.”
Optimizing for Mini Sitelinks
I do know of no option to optimize for branded sitelinks aside from altering a website’s major navigation. (Paid search advertisers have significantly better management.) However there are few on-page ways to generate mini sitelinks, which seem in two varieties.
- Bounce-to sitelinks go on to a piece of the identical web page rating for the search question.
- Cross-site sitelinks go to different pages of the location associated to the question.
Bounce-to sitelinks are based mostly on inserting so-called “HTML anchor hyperlinks” on a web page after which linking to them. Clicking a hyperlink takes the customer to that anchor with out opening a brand new web page.
WPBeginner explains how WordPress customers can simply create a clickable desk of contents through anchor texts in H2 or H3 subheadings. Right here’s a screenshot under of a web page that generates natural mini sitelinks utilizing that technique.
Take into account updating a web page if it features a desk of contents however fails to generate mini sitelinks on Google’s search outcomes. In my expertise, Google generally drops sitelinks if the content material is a few years previous.
Cross-site sitelinks present up when the underlying web page hyperlinks internally to others that elaborate on the subject. That is helpful for highly-focused content material.
Take into account, too, linking prominently from one web page to subheadings on one other. Right here’s an instance of cross-site sitelinks on Google search outcomes.
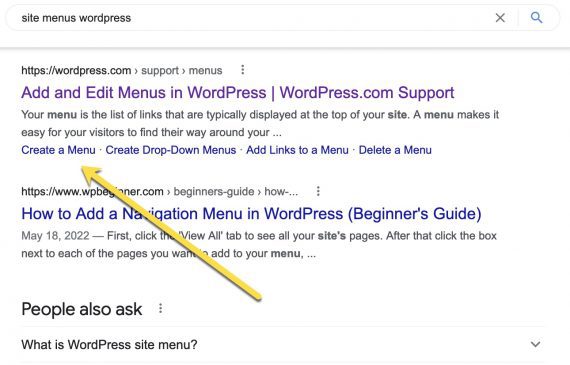
Cross-site sitelinks present up when the underlying web page hyperlinks internally to others that elaborate on the subject, corresponding to this instance of including menus in WordPress.
And right here’s the web page that populates them. As you may see, Google usually drops some hyperlinks and re-orders others.
Cross-site sitelinks are tougher to earn as a result of they (apparently) depend on web page authority, i.e., its backlink profile. Monitor your sitelinks utilizing SE Rating’s “Sitelinks” filter inside its place monitoring device. Save the filter for simpler subsequent entry.
Tips on how to Take away a Sitelink
A typical purpose to take away a sitelink is to exchange it with one other web page. Sadly, Google offers few, if any, removing choices.
- Search Console now not provides management over sitelinks. It used to.
- Google recommends utilizing a noindex meta tag to eradicate a sitelink. That advice, nonetheless, is extremely damaging. It is going to take away all the web page from Google’s index, stopping it from rating for any question.
- Lastly, this meta tag continues to be (apparently) supported by Google: <meta identify=”google” content material=”nositelinkssearchbox”/>. This can take away the “sitelinks search field” out of your search snippet, however I’m not certain if it’s going to eradicate a web page (from sitelinks). It’s price a strive if you happen to’re determined.