When the acorn that will turn out to be the search engine optimization trade began to develop, indexing and rating at search engines like google had been each primarily based purely on key phrases.
The search engine would match key phrases in a question to key phrases in its index parallel to key phrases that appeared on a webpage.
Pages with the very best relevancy rating could be ranked so as utilizing one of many three hottest retrieval methods:
- Boolean Mannequin
- Probabilistic Mannequin
- Vector House Mannequin
The vector house mannequin grew to become essentially the most related for search engines like google.
I’m going to revisit the fundamental and considerably easy clarification of the traditional mannequin I used again within the day on this article (as a result of it’s nonetheless related within the search engine combine).
Alongside the best way, we’ll dispel a fable or two – such because the notion of “key phrase density” of a webpage. Let’s put that one to mattress as soon as and for all.
The key phrase: Probably the most generally used phrases in data science; to entrepreneurs – a shrouded thriller
“What’s a key phrase?”
You don’t have any thought what number of instances I heard that query when the search engine optimization trade was rising. And after I’d given a nutshell of an evidence, the follow-up query could be: “So, what are my key phrases, Mike?”
Actually, it was fairly tough making an attempt to elucidate to entrepreneurs that particular key phrases utilized in a question had been what triggered corresponding webpages in search engine outcomes.
And sure, that will nearly definitely elevate one other query: “What’s a question, Mike?”
As we speak, phrases like key phrase, question, index, rating and all the remainder are commonplace within the digital advertising lexicon.
Nonetheless, as an search engine optimization, I imagine it’s eminently helpful to grasp the place they’re drawn from and why and the way these phrases nonetheless apply as a lot now as they did again within the day.
The science of data retrieval (IR) is a subset underneath the umbrella time period “synthetic intelligence.” However IR itself can be comprised of a number of subsets, together with that of library and knowledge science.
And that’s our place to begin for this second a part of my wander down search engine optimization reminiscence lane. (My first, in case you missed it, was: We’ve crawled the online for 32 years: What’s modified?)
This ongoing collection of articles is predicated on what I wrote in a guide about search engine optimization 20 years in the past, making observations concerning the state-of-the-art over time and evaluating it to the place we’re as we speak.
The little previous girl within the library
So, having highlighted that there are parts of library science underneath the Info Retrieval banner, let me relate the place they match into net search.
Seemingly, librarians are primarily recognized as little previous girls. It definitely appeared that manner once I interviewed a number of main scientists within the rising new area of “net” Info Retrial (IR) all these years in the past.
Brian Pinkerton, inventor of WebCrawler, together with Andrei Broder, Vice President Know-how and Chief Scientist with Alta Vista, the primary search engine earlier than Google and certainly Craig Silverstein, Director of Know-how at Google (and notably, Google worker primary) all described their work on this new area as making an attempt to get a search engine to emulate “the little previous girl within the library.”
Libraries are primarily based on the idea of the index card – the unique function of which was to try to arrange and classify each identified animal, plant, and mineral on the planet.
Index playing cards shaped the spine of the complete library system, indexing huge and different quantities of data.
Other than the title of the writer, title of the guide, material and notable “index phrases” (a.ok.a., key phrases), and so on., the index card would even have the placement of the guide. And due to this fact, after some time “the little previous girl librarian” whenever you requested her a few explicit guide, would intuitively be capable of level not simply to the part of the library, however most likely even the shelf the guide was on, offering a customized fast retrieval technique.
Nonetheless, once I defined the similarity of that kind of indexing system at search engines like google as I did all these years again, I had so as to add a caveat that’s nonetheless essential to know:
“The most important search engines like google are index primarily based in an analogous method to that of a library. Having saved a big fraction of the online in large indices, they then have to shortly return related paperwork in opposition to a given key phrase or phrase. However the variation of net pages, by way of composition, high quality, and content material, is even larger than the dimensions of the uncooked information itself. The net as a complete has no unifying construction, with an infinite variant within the model of authoring and content material far wider and extra advanced than in conventional collections of textual content paperwork. This makes it nearly unattainable for a search engine to use strictly typical methods utilized in libraries, database administration methods, and knowledge retrieval.”
Inevitably, what then occurred with key phrases and the best way we write for the online was the emergence of a brand new area of communication.
As I defined within the guide, HTML could possibly be considered as a brand new linguistic style and needs to be handled as such in future linguistic research. There’s far more to a Hypertext doc than there may be to a “flat textual content” doc. And that offers extra of a sign to what a specific net web page is about when it’s being learn by people in addition to the textual content being analyzed, categorized, and categorized by means of textual content mining and knowledge extraction by search engines like google.
Typically I nonetheless hear SEOs referring to search engines like google “machine studying” net pages, however that time period belongs far more to the comparatively latest introduction of “structured information” methods.
As I incessantly nonetheless have to elucidate, a human studying an online web page and search engines like google textual content mining and extracting data “about” a web page isn’t the identical factor as people studying an online web page and search engines like google being” fed” structured information.
The most effective tangible instance I’ve discovered is to make a comparability between a contemporary HTML net web page with inserted “machine readable” structured information and a contemporary passport. Check out the image web page in your passport and also you’ll see one predominant part together with your image and textual content for people to learn and a separate part on the backside of the web page, which is created particularly for machine studying by swiping or scanning.
Quintessentially, a contemporary net web page is structured sort of like a contemporary passport. Curiously, 20 years in the past I referenced the person/machine mixture with this little factoid:
“In 1747 the French doctor and thinker Julien Offroy de la Mettrie revealed one of the seminal works within the historical past of concepts. He entitled it L’HOMME MACHINE, which is greatest translated as “man, a machine.” Typically, you’ll hear the phrase ‘of males and machines’ and that is the basis thought of synthetic intelligence.”
I emphasised the significance of structured information in my earlier article and do hope to put in writing one thing for you that I imagine can be vastly useful to grasp the steadiness between people studying and machine studying. I completely simplified it this fashion again in 2002 to supply a fundamental rationalization:
- Knowledge: a illustration of information or concepts in a formalized method, able to being communicated or manipulated by some course of.
- Info: the which means {that a} human assigns to information by way of the identified conventions utilized in its illustration.
Due to this fact:
- Knowledge is expounded to information and machines.
- Info is expounded to which means and people.
Let’s speak concerning the traits of textual content for a minute after which I’ll cowl how textual content might be represented as information in one thing “considerably misunderstood” (let’s say) within the search engine optimization trade known as the vector house mannequin.
An important key phrases in a search engine index vs. the most well-liked phrases
Ever heard of Zipf’s Legislation?
Named after Harvard Linguistic Professor George Kingsley Zipf, it predicts the phenomenon that, as we write, we use acquainted phrases with excessive frequency.
Zipf mentioned his legislation is predicated on the primary predictor of human habits: striving to reduce effort. Due to this fact, Zipf’s legislation applies to nearly any area involving human manufacturing.
This implies we even have a constrained relationship between rank and frequency in pure language.
Most giant collections of textual content paperwork have related statistical traits. Understanding about these statistics is useful as a result of they affect the effectiveness and effectivity of information constructions used to index paperwork. Many retrieval fashions depend on them.
There are patterns of occurrences in the best way we write – we usually search for the best, shortest, least concerned, quickest technique attainable. So, the reality is, we simply use the identical easy phrases again and again.
For instance, all these years again, I got here throughout some statistics from an experiment the place scientists took a 131MB assortment (that was huge information again then) of 46,500 newspaper articles (19 million time period occurrences).
Right here is the info for the highest 10 phrases and what number of instances they had been used inside this corpus. You’ll get the purpose fairly shortly, I feel:
Phrase frequency
the: 1130021
of 547311
to 516635
a 464736
in 390819
and 387703
that 204351
for 199340
is 152483
mentioned 148302
Keep in mind, all of the articles included within the corpus had been written by skilled journalists. However for those who take a look at the highest ten most incessantly used phrases, you might hardly make a single wise sentence out of them.
As a result of these widespread phrases happen so incessantly within the English language, search engines like google will ignore them as “cease phrases.” If the most well-liked phrases we use don’t present a lot worth to an automatic indexing system, which phrases do?
As already famous, there was a lot work within the area of data retrieval (IR) methods. Statistical approaches have been broadly utilized due to the poor match of textual content to information fashions primarily based on formal logics (e.g., relational databases).
So quite than requiring that customers will be capable of anticipate the precise phrases and combos of phrases that will seem in paperwork of curiosity, statistical IR lets customers merely enter a string of phrases which are prone to seem in a doc.
The system then takes under consideration the frequency of those phrases in a set of textual content, and in particular person paperwork, to find out which phrases are prone to be the perfect clues of relevance. A rating is computed for every doc primarily based on the phrases it incorporates and the very best scoring paperwork are retrieved.
I used to be lucky sufficient to Interview a number one researcher within the area of IR when researching myself for the guide again in 2001. At the moment, Andrei Broder was Chief Scientist with Alta Vista (presently Distinguished Engineer at Google), and we had been discussing the subject of “time period vectors” and I requested if he may give me a easy clarification of what they’re.
He defined to me how, when “weighting” phrases for significance within the index, he might observe the incidence of the phrase “of” thousands and thousands of instances within the corpus. This can be a phrase which goes to get no “weight” in any respect, he mentioned. But when he sees one thing just like the phrase “hemoglobin”, which is a a lot rarer phrase within the corpus, then this one will get some weight.
I wish to take a fast step again right here earlier than I clarify how the index is created, and dispel one other fable that has lingered over time. And that’s the one the place many individuals imagine that Google (and different search engines like google) are literally downloading your net pages and storing them on a tough drive.
Nope, by no means. We have already got a spot to try this, it’s known as the world vast net.
Sure, Google maintains a “cached” snapshot of the web page for fast retrieval. However when that web page content material modifications, the following time the web page is crawled the cached model modifications as nicely.
That’s why you may by no means discover copies of your previous net pages at Google. For that, your solely actual useful resource is the Web Archive (a.ok.a., The Wayback Machine).
Actually, when your web page is crawled it’s mainly dismantled. The textual content is parsed (extracted) from the doc.
Every doc is given its personal identifier together with particulars of the placement (URL) and the “uncooked information” is forwarded to the indexer module. The phrases/phrases are saved with the related doc ID by which it appeared.
Right here’s a quite simple instance utilizing two Docs and the textual content they comprise that I created 20 years in the past.
Recall index development

After all of the paperwork have been parsed, the inverted file is sorted by phrases:
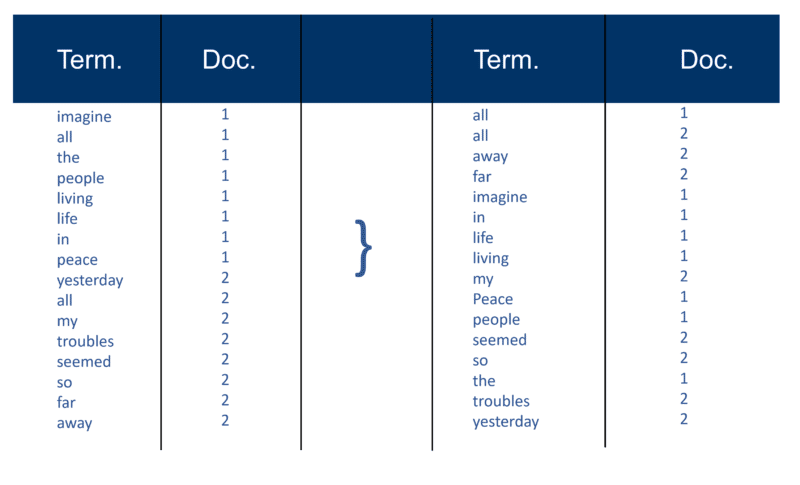
In my instance this seems pretty easy in the beginning of the method, however the postings (as they’re identified in data retrieval phrases) to the index go in a single Doc at a time. Once more, with thousands and thousands of Docs, you may think about the quantity of processing energy required to show this into the large ‘time period clever view’ which is simplified above, first by time period after which by Doc inside every time period.
You’ll observe my reference to “thousands and thousands of Docs” from all these years in the past. After all, we’re into billions (even trillions) as of late. In my fundamental clarification of how the index is created, I continued with this:
Every search engine creates its personal customized dictionary (or lexicon as it’s – keep in mind that many net pages should not written in English), which has to incorporate each new ‘time period’ found after a crawl (take into consideration the best way that, when utilizing a phrase processor like Microsoft Phrase, you incessantly get the choice so as to add a phrase to your individual customized dictionary, i.e. one thing which doesn’t happen in the usual English dictionary). As soon as the search engine has its ‘huge’ index, some phrases can be extra essential than others. So, every time period deserves its personal weight (worth). Quite a lot of the weighting issue is determined by the time period itself. After all, that is pretty straight ahead when you consider it, so extra weight is given to a phrase with extra occurrences, however this weight is then elevated by the ‘rarity’ of the time period throughout the entire corpus. The indexer also can give extra ‘weight’ to phrases which seem in sure locations within the Doc. Phrases which appeared within the title tag <title> are essential. Phrases that are in <h1> headline tags or these that are in daring <b> on the web page could also be extra related. The phrases which seem within the anchor textual content of hyperlinks on HTML pages, or near them are definitely considered as essential. Phrases that seem in <alt> textual content tags with pictures are famous in addition to phrases which seem in meta tags.
Other than the unique textual content “Trendy Info Retrieval” written by the scientist Gerard Salton (considered the daddy of contemporary data retrieval) I had quite a lot of different sources again within the day who verified the above. Each Brian Pinkerton and Michael Maudlin (inventors of the various search engines WebCrawler and Lycos respectively) gave me particulars on how “the traditional Salton strategy” was used. And each made me conscious of the constraints.
Not solely that, Larry Web page and Sergey Brin highlighted the exact same within the authentic paper they wrote on the launch of the Google prototype. I’m coming again to this because it’s essential in serving to to dispel one other fable.
However first, right here’s how I defined the “traditional Salton strategy” again in 2002. You should definitely observe the reference to “a time period weight pair.”
As soon as the search engine has created its ‘huge index’ the indexer module then measures the ‘time period frequency’ (tf) of the phrase in a Doc to get the ‘time period density’ after which measures the ‘inverse doc frequency’ (idf) which is a calculation of the frequency of phrases in a doc; the entire variety of paperwork; the variety of paperwork which comprise the time period. With this additional calculation, every Doc can now be considered as a vector of tf x idf values (binary or numeric values corresponding straight or not directly to the phrases of the Doc). What you then have is a time period weight pair. You could possibly transpose this as: a doc has a weighted listing of phrases; a phrase has a weighted listing of paperwork (a time period weight pair).
The Vector House Mannequin

Now that the Docs are vectors with one element for every time period, what has been created is a ‘vector house’ the place all of the Docs dwell. However what are the advantages of making this universe of Docs which all now have this magnitude?
On this manner, if Doc ‘d’ (for example) is a vector then it’s straightforward to search out others prefer it and likewise to search out vectors close to it.
Intuitively, you may then decide that paperwork, that are shut collectively in vector house, discuss the identical issues. By doing this a search engine can then create clustering of phrases or Docs and add varied different weighting strategies.
Nonetheless, the primary advantage of utilizing time period vectors for search engines like google is that the question engine can regard a question itself as being a really brief Doc. On this manner, the question turns into a vector in the identical vector house and the question engine can measure every Doc’s proximity to it.
The Vector House Mannequin permits the consumer to question the search engine for “ideas” quite than a pure “lexical” search. As you may see right here, even 20 years in the past the notion of ideas and subjects versus simply key phrases was very a lot in play.
OK, let’s deal with this “key phrase density” factor. The phrase “density” does seem within the clarification of how the vector house mannequin works, however solely because it applies to the calculation throughout the complete corpus of paperwork – to not a single web page. Maybe it’s that reference that made so many SEOs begin utilizing key phrase density analyzers on single pages.
I’ve additionally observed over time that many SEOs, who do uncover the vector house mannequin, are likely to try to apply the traditional tf x idf time period weighting. However that’s a lot much less prone to work, notably at Google, as founders Larry Web page and Sergey Brin said of their authentic paper on how Google works – they emphasize the poor high quality of outcomes when making use of the traditional mannequin alone:
“For instance, the usual vector house mannequin tries to return the doc that almost all intently approximates the question, on condition that each question and doc are vectors outlined by their phrase incidence. On the net, this technique usually returns very brief paperwork which are solely the question plus just a few phrases.”
There have been many variants to try to get across the ‘rigidity’ of the Vector House Mannequin. And over time with advances in synthetic intelligence and machine studying, there are numerous variations to the strategy which might calculate the weighting of particular phrases and paperwork within the index.
You could possibly spend years making an attempt to determine what formulae any search engine is utilizing, not to mention Google (though you might be certain which one they’re not utilizing as I’ve simply identified). So, bearing this in thoughts, it ought to dispel the parable that making an attempt to govern the key phrase density of net pages whenever you create them is a considerably wasted effort.
Fixing the abundance drawback
The primary era of search engines like google relied closely on on-page elements for rating.
However the issue you’ve got utilizing purely keyword-based rating methods (past what I simply talked about about Google from day one) is one thing referred to as “the abundance drawback” which considers the online rising exponentially on daily basis and the exponential development in paperwork containing the identical key phrases.
And that poses the query on this slide which I’ve been utilizing since 2002:

You possibly can assume that the orchestra conductor, who has been arranging and taking part in the piece for a few years with many orchestras, could be essentially the most authoritative. However working purely on key phrase rating methods solely, it’s simply as doubtless that the music pupil could possibly be the primary outcome.
How do you remedy that drawback?
Properly, the reply is hyperlink evaluation (a.ok.a., backlinks).
In my subsequent installment, I’ll clarify how the phrase “authority” entered the IR and search engine optimization lexicon. And I’ll additionally clarify the unique supply of what’s now known as E-A-T and what it’s truly primarily based on.
Till then – be nicely, keep secure and keep in mind what pleasure there may be in discussing the interior workings of search engines like google!
Opinions expressed on this article are these of the visitor writer and never essentially Search Engine Land. Employees authors are listed right here.
New on Search Engine Land




