A trio of e-mail authentication requirements work collectively to enhance e-mail deliverability for the sender and e-mail security for the recipient.
Sender Coverage Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Recognized Mail (DKIM), and Area-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) assist to make sure that emails despatched out of your firm are actual and that malicious actors will not be spoofing or in any other case tampering with them.
SPF, DKIM, DMARC
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC present the receiving e-mail server {that a} given message was despatched from a certified IP deal with, that the sender is genuine, and that the sender is clear about its id.
Let’s take each in flip.
Organising SPF information on your area entails including a kind of TXT report containing a certified record of outgoing mail servers to the Area Identify System (DNS). SPF verifies that emails from your enterprise’s area come from an authenticated supply, not an imposter.
DKIM keys encompass two elements: a public key saved within the DNS and a non-public key saved on the sending mail server. The DKIM signature connected to every outgoing e-mail is utilized by recipients’ mail servers to confirm its authenticity. DKIM can even point out if a given e-mail message has been altered.
DMARC is a coverage mechanism that enables an organization to manage how incoming emails from its area must be dealt with in the event that they fail the SPF or DKIM authentication. The choices are “reject,” “quarantine,” or “none.” This may be like an alarm bell if a wrong-doer is making an attempt to make use of your area.
SPF Data
Organising an SPF report requires entry to your area’s DNS information on the registrar, comparable to GoDaddy or comparable. If in case you have ever needed to confirm your area or transfer it to a brand new server you probably up to date its DNS report.
An SPF report is just a TXT report in your area’s DNS.
The SPF report shall be of the kind “TXT.” And it’ll begin with the model of SPF you’re utilizing.
v=spf1
The model is adopted by a listing of licensed IP4 or IP6 addresses, as in:
v=spf1 ip4:192.168.0.1
This SPF report would authorize emails from the 192.168.0.1 IP deal with. To permit a variety of IP addresses, you would use Classless Inter-Area Routing (CIDR) notation (generally referred to as “slash” notation).
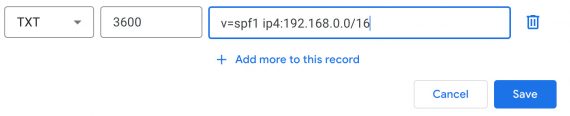
v=spf1 ip4:192.168.0.0/16
The above SPF report would authorize a variety of IP addresses from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 — that is what the “/16” signifies.
Utilizing the prefix “a,” an SPF report can authorize a website by identify. The report under authorizes a server related to the instance.com area.
v=spf1 a:instance.com
Equally, the prefix “mx” (“mail change”) authorizes particular mail servers.
v=spf1 mx:mail.instance.com
To authorize a third-party sender, use the prefix “embrace.” The instance under permits each an IP vary and Google servers.
v=spf1 ip4:192.168.0.0/16 embrace:_spf.google.com
There are additionally two SPF qualifiers. The primary is ~all with a tilde (~). The second is -all with a hyphen (-).
The tilde model (~all) is a soft-fail qualifier. Normally, the receiving e-mail server will settle for messages from senders that aren’t within the related SPF report however contemplate them to be suspicious.
The hyphen model (-all) is a hard-fail qualifier. The receiving e-mail server will probably label messages despatched from a server not licensed within the SPF report as spam and reject them.
Lastly, all of those could also be used collectively for comparatively advanced authorizations.
v=spf1 ip4:192.168.0.0/16 a:instance.com embrace:_spf.google.com
Bear in mind, SPF information assist the receiving e-mail servers determine genuine e-mail messages out of your firm’s area.
DKIM Keys
DKIM protects your area and helps to forestall anybody from impersonating your organization. The 2 DKiM keys permit the recipient’s e-mail server to confirm that your organization despatched the message and that it was not altered after you despatched it.
Step one in organising DKIM is producing the keys — one public and one personal. The personal key’s safe on the server used for sending emails out of your area. The general public key’s added to the DNS as a TXT report.
The difficult half is producing the keys because the actual process for creating them varies from one e-mail service supplier to the following. And it’s fully completely different if your organization hosts its personal mail server.
E mail service suppliers supply directions. Listed here are a number of examples in no explicit order.
- Mailchimp: Set Up E mail Area Authentication,
- Klaviyo: How one can Arrange a Devoted Sending Area,
- Zoho Campaigns: How one can Authenticate My Area,
- MailerLite: E mail area authentication,
- Campaigner: DKIM, SPF, and DMARC,
- ConvertKit: Utilizing a Verified Area for E mail Sending,
- MailUp: Maximizing Deliverability for Your Emails,
- ActiveCampaign: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Authentication,
- Keap: DKIM.
In every case, the DKIM is accomplished whenever you add — copy and paste — the e-mail supplier’s CNAME report to your area’s DNS. This report(s) represents the general public key to authenticate your organization’s outbound e-mail advertising messages.
DMARC
DMARC supplies one other layer of safety and in addition instructs e-mail servers what to do with messages that fail SPF or DKIM authentication.
The inspiration of DMARC is a TXT report positioned in your area’s DNS. This can include the DMARC coverage with no less than two components:
- An e-mail deal with to obtain combination studies of e-mail authentication, and
- The motion to tackle emails that fail authentication (i.e., reject or quarantine).
Right here’s an instance DMARC TXT report in a DNS:
v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; rua=mailto:armando@instance.com; ruf=mailto:armando@instance.com.
The report begins with the DMARC model.
v=DMARC1;
The “p” factor assigns the motion for emails that fail authentication. On this case, it’s set to “quarantine,” which instructs the receiving server to maneuver such messages to a holding space. Different choices embrace “none” — which doesn’t cease the e-mail however screens SPF or DKIM failures — or “reject.”
p=quarantine;
The prefixes “rua” and “ruf” inform the receiving server the place to ship combination studies (rua — Reporting URI for Combination information) and forensic studies (ruf — Reporting URI for Failure information). These studies can disclose a felony making an attempt to impersonate your enterprise.
Further modifiers embrace:
- pct — the proportion of e-mail messages subjected to the DMARC coverage.
- sp — the DMARC coverage for subdomains.
- adkim — assigns strict (adkim:s) or relaxed (adkim:r) mode for DKIM.
- aspf — assigns strict (adkim:s) or relaxed (adkim:r) mode for SPF.
Third-party companies might help generate a DMARC report based mostly on the official customary. These companies embrace:
Defend Sender and Recipients
Organising SPF, DKIM, and DMARC information on your area ensures that e-mail servers acknowledge messages out of your firm as genuine and reject imposters. The consequence protects your organization’s status and shields clients from phishing assaults and different forms of e-mail fraud.



