It was 12 years in the past in the present day that Google launched the Panda replace. This algorithm replace had a large and far-reaching influence on search engine marketing and content material methods for years to return.
Right here’s an entire historical past of the Google Panda algorithm replace.
What was the Google Panda replace?
Google Panda was a significant algorithm replace that impacted search rankings for 11.8% of queries within the U.S.
Google mentioned Panda was designed to scale back the rankings for low-quality websites (“websites that are low-value add for customers, copy content material from different web sites or websites which might be simply not very helpful”) and reward higher rankings to high-quality websites (“websites with unique content material and knowledge reminiscent of analysis, in-depth studies, considerate evaluation and so forth”).
The algorithm formally began rolling out on Feb. 23, 2011, nevertheless it wasn’t till Feb. 24, 2011, that we realized about it.
Panda didn’t solely influence content material farms. Web sites of all sizes, throughout industries, felt the wrath of Panda.
There have been a number of studies of corporations going out of enterprise as a result of they’d relied on Google visitors for years. As soon as that natural visitors was gone, so was their enterprise.
After its preliminary launch, Google introduced a number of refreshes and updates to Panda on a near-monthly foundation for the subsequent two years (9 in 2011 and 14 in 2012). You’ll find an entire timeline and our protection of these updates on the finish of this information.
One factor Google Panda was not: a penalty. Web sites impacted by the Google Panda Replace have been downgraded algorithmically. This implies no Google worker took handbook motion to trigger the decrease rankings.
For anybody hit by Panda, it in all probability felt like a penalty. However Google doesn’t take into account downgrading rankings for a web site algorithmically as a “penalty.”
Why was Google Panda launched?
The primary goal of Google Panda was low-quality content material. In 2011, Google was looking for an answer for its content material farm drawback.
In case you’re not acquainted with the time period, a “content material farm” was a web site that paid freelance writers (usually poorly) to pump out as a lot content material as quick as attainable. The only purpose for these corporations was to rank extraordinarily properly in Google’s search outcomes for high-traffic key phrases. Article high quality was usually low.
These excessive rankings meant these content material farms acquired a number of visitors. They usually monetized that visitors through show promoting (mockingly, lots of these websites have been utilizing Google AdSense.) Demand Media might be the very best instance of the traditional content material farm mannequin. Suite 101 was one other massive content material farm.
Apparently, most of the content material points Google was making an attempt to resolve in 2010 had come about after the Caffeine Replace. Google was now crawling content material quicker, and its index grew quickly. But it surely additionally meant some “shallow” content material was rating prominently.
Enterprise Insider even revealed an article with this slightly blunt headline: Google’s Search Algorithm Has Been Ruined, Time To Transfer Again To Curation.” On TechCrunch, there was: “Why We Desperately Want a New (and Higher) Google.”
Nicely, on Feb. 24, 2011, Google rocked the world of content material farms – and the whole search engine marketing business. Google now had a approach to search for alerts that differentiate high-quality and low-quality websites.
Get the each day e-newsletter search entrepreneurs depend on.
Why did Google identify it Panda?
In an interview with Wired, Amit Singhal, head of Google search, revealed the place the Panda identify got here from:
“Nicely, we named it internally after an engineer, and his identify is Panda. So internally we known as an enormous Panda. He was one of many key guys. He principally got here up with the breakthrough just a few months again that made it attainable.”
– Google’s Amit Singhal in 2011
The total identify of that Google engineer is Navneet Panda.
Nonetheless, the replace wasn’t known as “Panda” outdoors of Google when it initially launched. Search Engine Land founder Danny Sullivan known as it the “Farmer’ replace – till the Panda identify was revealed in Wired. So in the event you see the Farmer identify pop up in any of our outdated protection of Panda, that is why.
Google Panda algorithm defined: the way it labored
A lot hypothesis adopted the arrival of Google Panda. Most of that’s irrelevant in the present day, so we cannot rehash the various Panda myths on this information.
Here is a rundown of what we realized about how Google Panda labored and what made it distinctive.
Panda was an algorithm utilized to websites
An important factor it is advisable to perceive about Panda is that it evaluates the general high quality of the whole web site.
Here is what Gary Illyes, Google webmaster developments analyst, instructed Search Engine Land in a 2016 interview:
“… we don’t consider Panda as a penalty now, however slightly as an algorithm utilized to websites … or websites as an entire.
It measures the standard of a website just about by trying on the overwhelming majority of the pages at the very least. However basically permits us to take high quality of the entire website under consideration when rating pages from that specific website and modify the rating accordingly for the pages.”
Google’s Gary Illyes, in 2016
So what Illyes confirmed is that Panda demotes content material, basically that means low-quality content material can hurt rating.
Google’s John Mueller additionally mentioned that Panda appears at website structure to evaluate web site high quality.
Did eradicating or bettering low-quality content material assist?
On March 8, 2011, Michael Wyszomierski, a member of the Google webspam staff, posted a message in a Webmaster Central assist discussion board thread:
“Our latest replace is designed to scale back rankings for low-quality websites, so the important thing factor for site owners to do is be certain their websites are the very best high quality attainable. We checked out quite a lot of alerts to detect low high quality websites. Keep in mind that individuals looking out on Google usually do not wish to see shallow or poorly written content material, content material that’s copied from different web sites, or info which might be simply not that helpful. As well as, it is vital for site owners to know that low high quality content material on a part of a website can influence a website’s rating as an entire. For that reason, in the event you consider you’ve got been impacted by this modification it is best to consider all of the content material in your website and do your greatest to enhance the general high quality of the pages in your area. Eradicating low high quality pages or shifting them to a special area might assist your rankings for the upper high quality content material.”
– Google’s Michael Wyszomierski, in 2011
What’s vital to notice right here about Panda:
- It could possibly determine content material that’s shallow, poorly written, or copied from different web sites.
- Poorly written content material can damage rankings.
- Eradicating low-quality pages from a part of a web site may help high-quality pages rank higher.
- Bettering content material (making it “helpful”) may help your rankings.
Afterward, Google tried to stroll again the thought of eradicating content material. Google began recommending including high-quality content material and fixing the low-quality content material as a substitute. That is most certainly as a result of many in search engine marketing began taking a metaphorical blowtorch to their content material as a substitute of a scalpel.
At SMX East 2017, Illyes mentioned pruning content material did not assist with Panda.
“It’s very possible that you just didn’t get Pandalyzed due to your low-quality content material. It’s extra about guaranteeing the content material that’s truly rating doesn’t rank increased than it ought to. … It undoubtedly doesn’t work with the present model of the core algorithm, and it could simply carry your visitors farther down. Panda principally disregards stuff you do to rank artificially. You need to spend assets on bettering content material as a substitute, however in the event you don’t have the means to do this, possibly take away it as a substitute.”
– Google’s Gary Illyes, in 2017
Google on the right way to consider whether or not a website was ‘high-quality’
On Might 6, 2011, Google revealed a listing of 23 questions to elucidate how Google searches for high-quality websites, to assist those who Panda had been negatively impacted:
- Would you belief the data offered on this article?
- Is this text written by an skilled or fanatic who is aware of the subject properly, or is it extra shallow in nature?
- Does the location have duplicate, overlapping, or redundant articles on the identical or related matters with barely completely different key phrase variations?
- Would you be snug giving your bank card info to this website?
- Does this text have spelling, stylistic, or factual errors?
- Are the matters pushed by real pursuits of readers of the location, or does the location generate content material by making an attempt to guess what would possibly rank properly in serps?
- Does the article present unique content material or info, unique reporting, unique analysis, or unique evaluation?
- Does the web page present substantial worth when in comparison with different pages in search outcomes?
- How a lot high quality management is finished on content material?
- Does the article describe each side of a narrative?
- Is the location a acknowledged authority on its subject?
- Is the content material mass-produced by or outsourced to a lot of creators, or unfold throughout a big community of websites, in order that particular person pages or websites don’t get as a lot consideration or care?
- Was the article edited properly, or does it seem sloppy or rapidly produced?
- For a well being associated question, would you belief info from this website?
- Would you acknowledge this website as an authoritative supply when talked about by identify?
- Does this text present an entire or complete description of the subject?
- Does this text comprise insightful evaluation or attention-grabbing info that’s past apparent?
- Is that this the kind of web page you’d wish to bookmark, share with a buddy, or advocate?
- Does this text have an extreme quantity of advertisements that distract from or intrude with the principle content material?
- Would you anticipate to see this text in a printed journal, encyclopedia or ebook?
- Are the articles brief, unsubstantial, or in any other case missing in useful specifics?
- Are the pages produced with nice care and a spotlight to element vs. much less consideration to element?
- Would customers complain once they see pages from this website?
Easy methods to get better from Panda
The massive query for anybody whose website was hit by Panda: How do I get better? Apart from pointing to the weblog put up with these 23 questions, Google supplied a little bit extra info over time.
On July 9, 2012, throughout a Google Search Central hangout from India, Google’s Matt Cutts mentioned it was attainable to get better 100%. How?
“Take a recent look and principally ask your self, ‘How compelling is my website?’ We’re searching for prime quality. We’re searching for one thing the place you land on it, you’re actually pleased, the kind of factor the place you wanna inform your mates about it and are available again to it, bookmark it. It’s simply extremely helpful.”
Google’s Matt Cutts in 2012
Here is the video:
Cutts additionally supplied some high-level perception in one other Google Search Central video launched Sept. 11, 2013:
“… the overriding type of purpose is to attempt to just remember to’ve acquired high-quality content material, the kind of content material that individuals actually take pleasure in, that’s compelling, the kind of factor that they’ll like to learn that you just would possibly see in {a magazine} or in a ebook, and that individuals would refer again to, or ship associates to, these types of issues,” Cutts mentioned. “So that might be the overriding purpose. …
So if you’re not rating as extremely as you have been up to now, general, it’s at all times a good suggestion to consider, OK, can I take a look at the standard of the content material on my website? Is there stuff that’s by-product, or scraped, or duplicate, and simply not as helpful?”
– Google’s Matt Cutts in 2013
Here is the video:
Panda consumed into Google’s core rating system
On Jan. 12, 2016, we reported that Panda had grow to be a part of Google’s core algorithm. Google by no means confirmed a precise date when this modified.
All we all know with 100% certainty is that it occurred in some unspecified time in the future in 2015 (in accordance with Google’s information to Google Search rating methods) after Google’s final confirmed Panda replace (4.2, on July 17, 2015).
In June 2016, Mueller mentioned that Google’s search engineers nonetheless tweaked points of Panda, nevertheless it was essentially the identical algorithm.
Panda was changed by Coati
Technically, Panda now not exists. That is as a result of Panda developed into a brand new algorithm known as Coati a while later.
Principally, Google Coati was the successor to the Panda algorithm. We realized this from Hyung-Jin Kim, the VP of Google Search, in November at SMX Subsequent 2022.
So regardless that it has been years since Panda was changed, Panda lived on by Coati, as a part of Google’s core algorithm.
The legacy of Google Panda
Google Panda remains to be impacting search engine marketing to this present day, greater than a decade after it launched. Listed below are simply three massive adjustments that got here from Panda:
- E-E-A-T. The idea of Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (plus the extra E for Expertise, as discovered within the high quality rater tips) could be traced again to the content material farm drawback. Google at all times needs to reward web sites that publish high-quality content material by specialists who’re authorities on a topic. The standard rater tips are the final word information for a way to not be a content material farm.
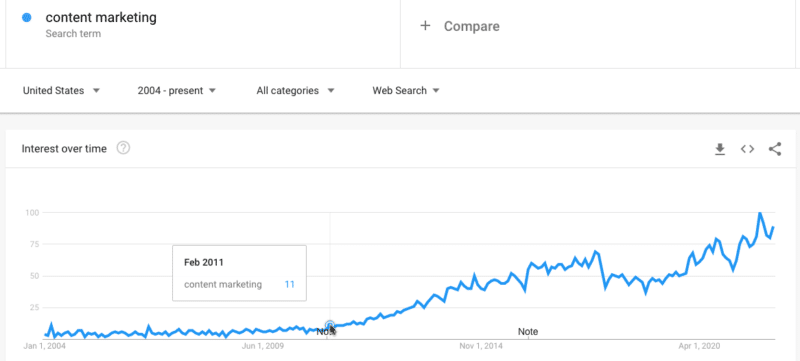
- Content material advertising and marketing. Content material advertising and marketing, as a time period, wasn’t actually a factor earlier than Panda. Simply go to Google Developments and you will see when the time period began gaining reputation, and never by coincidence. The time period itself could date again to 1996 (and the idea itself is as outdated as advertising and marketing), however content material advertising and marketing as its personal factor was basically born because of Panda.
- Differentiate or die. Maybe the most important classes popping out of Google Panda was to by no means put all of your eggs in a single basket. Particularly not Google’s. Counting on anybody channel for all, or almost all, of your visitors and revenue will not be a marketing strategy. It’s a gamble. By no means depart your self on the mercy of anybody channel. or platform – as a result of you don’t have any management over a third-party. If one algorithm change can wipe our your whole firm in a single day, you are doing it improper.
An entire timeline of the Google Panda Updates
Beneath is the entire record of all 28 confirmed Panda updates and refreshes. Oh, and since we did not get into the distinction between an replace versus a refresh, here is what which means: an replace was a change to the Google Panda algorithm, whereas a refresh meant Google reapplied all the identical alerts from the latest replace.
Here is Search Engine Land’s protection of Panda, from 2011 to 2016:



