“301” is an HTTP standing code for a everlasting redirect from one URL to a different. 301 redirects usually point out a web page has been moved, deleted, or up to date — sending guests and search bots to the brand new URL.
301 redirects are important for website rebrands and restructures to protect visitors and exterior backlinks.
Regardless of their significance, 301s redirects can do extra hurt than good if improperly executed.
Hyperlink Fairness
Google’s founding premise for natural rankings was primarily based on the quantity and high quality of hyperlinks to a web page — i.e., hyperlink fairness. However what occurs to rankings when the web page is 301-redirected to a different?
Ten years in the past, Google’s Matt Cutts mentioned a 301 redirect reduces a small quantity of hyperlink fairness.
Then, in 2016, Moz printed a case research addressing how a lot is misplaced. Per the research, a 301 redirect causes a 15% drop in natural visitors. A series of redirects — web page A redirects to web page B which redirects to web page C — produces a 15% discount for every one.
The research redirected a web page from /barstool.html to /bar-tool.html to /29-inch-bar-stool.html. The outcome was a constant lack of natural visitors.
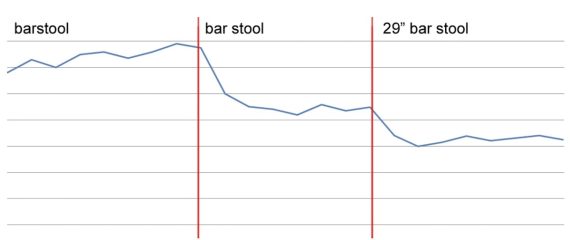
Moz’s research redirected a web page from /barstool.html to /bar-tool.html to /29-inch-bar-stool.html. The outcome was a constant lack of natural visitors.
Furthermore, there was no proof of restoration months afterward.
In 2022, Google’s John Mueller kind of confirmed that 301 redirects can scale back hyperlink fairness, stating it’s greatest to replace hyperlinks quite than redirect them.
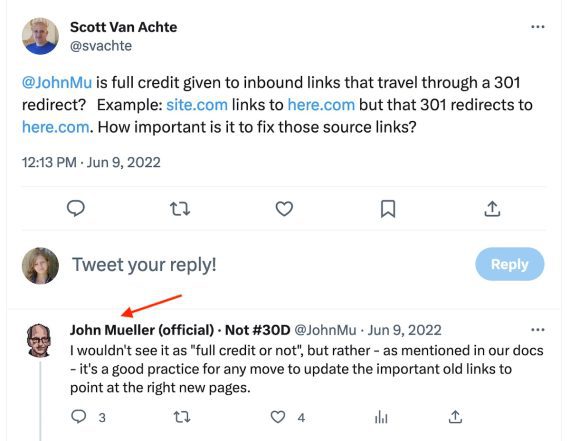
Google’s John Mueller implied in 2022 that 301 redirects can scale back hyperlink fairness, stating it’s an excellent follow to replace hyperlinks quite than redirect them.
1:1 Replacements
Mueller tweeted in 2017 that redirects needs to be used for “1:1 alternative URLs” — presumably redesigns and rebrands. A 301 redirect to an unrelated web page may lead to Google passing no hyperlink fairness, similar to a standing code “404,” signaling the web page now not exists.
Therefore, don’t redirect the web page of an expired product even when the brand new product is analogous. Let the expired product web page say “Offered out” and embody a hyperlink on that web page for the brand new merchandise. Sure, it’s an additional step for buyers, however it prevents confusion from touchdown on an surprising web page. And it preserves a minimum of a little bit of hyperlink fairness.
Dos and Don’ts
Right here’s how I’ve come to make use of 301 redirects after a decade of web optimization.
- Keep away from URL modifications if potential. I’ve by no means seen a redirected web page fully retain its unique rating.
- Keep away from 301s for inner hyperlinks. When altering a website’s area title or construction, change all inner hyperlinks to the brand new URLs. By no means redirect them.
- Replace a web page earlier than redirecting it. If it’s worthwhile to redirect a web page, replace its content material to match the brand new web page and let Google index the unique URL. Then, redirect it. That can allow Google to know each pages are an identical and go hyperlink fairness by the redirect. Likewise, for a brand new area title, replace the content material of the outdated website to match the brand new one. Let Google crawl the outdated website earlier than redirecting it. Assist Google perceive the redirects are for actual replacements.
- Beware of buying a website for the backlinks. Assume twice earlier than shopping for a website to redirect its hyperlink fairness. The redirects won’t probably work except the pages are practically an identical.
Implementing 301s
Organising a 301 redirect is deceptively simple. Plugins for WordPress and apps for Shopify seem to do the job with no developer. However these shortcuts will not be failsafe.
Inadvertently omitting hyperlinks — inner or exterior — could cause severe rating drops. By no means implement 301s with no complete technique involving content material updates, maps of outdated and new URLs, and thorough checking afterward.




