
There are many metrics that SEO (search engine optimisation) consultants use to gauge web site efficiency.
These metrics, resembling natural visitors and bounce fee, may be rating components for search engine outcomes pages (SERPs). That’s solely the case, nevertheless, if these pages are being correctly crawled, listed, and ranked.
So, how will you ensure that’s even the case? With crawl stats.
On this submit, I’ll pull again the curtain on how crawl stats perform. I’ll cowl how crawlbots are crawling your website and, extra importantly, how your website is responding. With this info, you’ll be able to then take steps to enhance crawlbot interactions for higher indexing and rating alternatives.
Crawl Response Key Findings
- Crawl response refers to how web sites reply to crawlbots.
- Internet crawlers, like crawlbot, analyze the robots.txt file and XML sitemap to grasp which pages to crawl and index.
- NP Digital analyzed 3 e-commerce shoppers (Consumer A, B, C) utilizing the Google Search Console (GSC) Crawl Stats report.
- OK (200) standing URLs dominate, adopted by 301 redirects.
- The common HTML file sort is 50%, and common JavaScript is 10%.
- Common goal breakdown: 33% discovery, 67% refresh.
- We advocate these finest practices based mostly on this evaluation:
- Cut back 404 errors by creating acceptable redirects.
- Select the proper redirect sort (non permanent or everlasting) and keep away from redirect chains.
- Consider the need of JavaScript file varieties for higher crawl efficiency.
- Use crawl goal percentages to make sure efficient indexing after web site adjustments.
What Is Crawl Response and What Is Its Function?
As an search engine optimisation skilled, you seemingly know the fundamentals of web site crawling, indexing, and rating; however did you ever marvel how web sites reply to crawlbots? This is called crawl response.
Extra particularly, a crawl response is the response that an online crawler, or crawlbot, receives from any given URL in your web site. Crawlbot will initially go in direction of the robots.txt file of a given web site. Usually, an XML sitemap is positioned throughout the robots.txt. The crawler then understands which pages must be crawled and listed, vs which mustn’t. The sitemap then lays out ALL of the web site’s pages. From there, the crawler heads to a web page and begins analyzing the web page and discovering new pages through hyperlinks.
When the crawlbot reaches out to your internet shopper with a web page request, the online shopper contacts the server, and the server “responds” in a single of some methods:
- OK (200): This means the URL was fetched efficiently and as anticipated.
- Moved everlasting (301): This means the URL was completely redirected to a brand new URL.
- Moved briefly (302): This means the URL was briefly redirected to a brand new URL.
- Not discovered (404): This means the request was acquired by the server, however the server couldn’t discover the web page that was requested.
There are different doable responses, however the above are the commonest.
Now, how about goal?
Crawl goal is the rationale why Google is crawling your website. There are two functions: discovery and refresh.
Discovery occurs when a crawl bot crawls a URL for the primary time. Refresh occurs when a crawlbot crawls a URL after it was beforehand crawled.
Throughout the GSC Crawl Stats report, goal is calculated as a share. There is no such thing as a good or dangerous share for both goal sort. Nonetheless, you need to use this part as a intestine test in opposition to your web site actions.
Should you’re a brand new web site that’s publishing tons of latest content material, then your discovery share goes to be larger for the primary few months. Should you’re an older web site that’s centered on updating beforehand revealed content material, then it is smart that your refresh share could be larger.
This crawl information plus file sort, are all obtainable in GSC so that you can use to your benefit. Happily, you don’t must be a GSC skilled to get essentially the most out of this device. I created this GSC skilled information to get you in control.
Crawl Response and E-Commerce: Our Findings
Generally, it’s not sufficient to understand how your web site is performing. As a substitute, it helps to match it to different web sites in your business to get an thought of the typical.
That approach, you’ll be able to examine your web site to the competitors to see the way it stacks up.
So how will you do this with an eye fixed in direction of Google crawling actions? With the Google Search Console Crawl Stats report!
Let me make clear: You possibly can solely analyze web sites on GSC if you personal it or have entry to the backend. Nonetheless, my workforce at NP Digital has carried out the heavy lifting for you. We’ve analyzed three of our shoppers’ top-ranking e-commerce web sites to find out the typical crawl response and crawl functions.
You need to use the knowledge we gleaned to match it to your individual web site’s GSC crawl stats report and see the way you measure up.
So, what did we discover?
Consumer A
First up is a dietary complement firm based mostly in Texas in america.
By Response
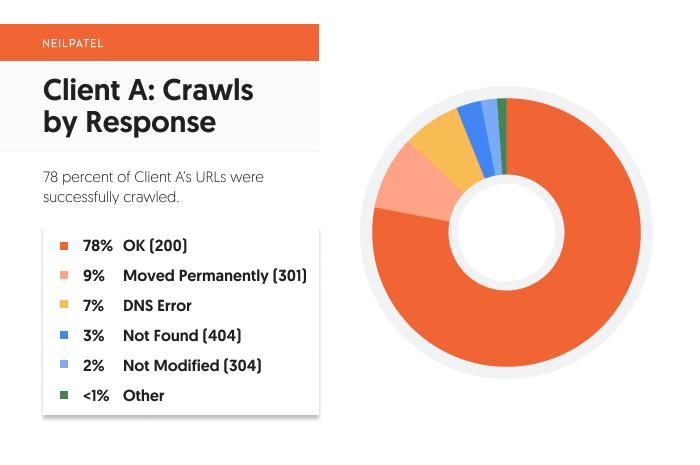
When trying on the breakdown by response for Consumer A, it’s a reasonably wholesome combine.
200 standing OK URLs are the biggest response, by far, at 78 %. Which means 78 % of the crawled URLs responded efficiently to the decision from the crawlbot.
One factor to notice right here is that 200 standing OK URLs may be listed and noindexed. An listed URL (the default) is one which crawlbots are inspired to each crawl and index. A noindexed URL is one which crawlbots can crawl, however they won’t index. In different phrases, they gained’t record the web page on Search Engine Outcomes Pages (SERPs).
If you wish to know what share of your 200 standing OK URLs are listed versus noindexed, you’ll be able to click on into the “By response” part in GSC and export the record of URLs:
You possibly can then carry that record over to a device like Screaming Frog to find out the quantity of listed versus noindexed URLs in your record.
Maybe you’re asking, “why does that matter?”
Let’s say that 200 standing OK URLs make up 75 % of your crawl response report with a complete variety of 100 URLs. If solely 50 % of these URLs are listed, that significantly cuts down the influence of your URLs on SERPs.
This information may help you to enhance your listed URL portfolio and its efficiency. How? which you can fairly influence simply 50 % of these 100 URLs. As a substitute of measuring your progress by analyzing all 100 URLs, you’ll be able to slim in on the 50 that you understand are listed.
Now on to the redirects.
9 % of the URLs are 301 (everlasting) redirects, whereas lower than one % are 302 (non permanent) redirects.
That’s an virtually 10 to 1 distinction between everlasting and non permanent redirects, and it’s what you’d anticipate to see on a wholesome area.
Why?
Momentary redirects are helpful in lots of instances, for instance, if you’re performing cut up testing or working a limited-time sale. Nonetheless, the bottom line is that they’re non permanent, so that they shouldn’t take up a big share of your responses.
On the flip facet, everlasting redirects are extra helpful for search engine optimisation. It is because a everlasting redirect tells crawlbots to index the newly focused URL and never the unique URL. This reduces crawl bloat over time and ensures extra individuals are directed to the proper URL first.
Final, let’s take a look at 404 URLs. For this shopper, they’re solely three % of the overall responses. Whereas the aim must be zero %, this at scale is usually very exhausting to realize.
So if zero % 404 URLs is unlikely, what are you able to do to make sure the client nonetheless has a very good expertise? A technique is by making a customized 404 web page that shows comparable choices (e.g., merchandise, weblog posts) for the customer to go to as a substitute, like this one from Clorox:
By File Sort
Let’s not neglect to think about the requests by file sort. That’s, the file sort during which the URL responds to the crawlbot’s request.
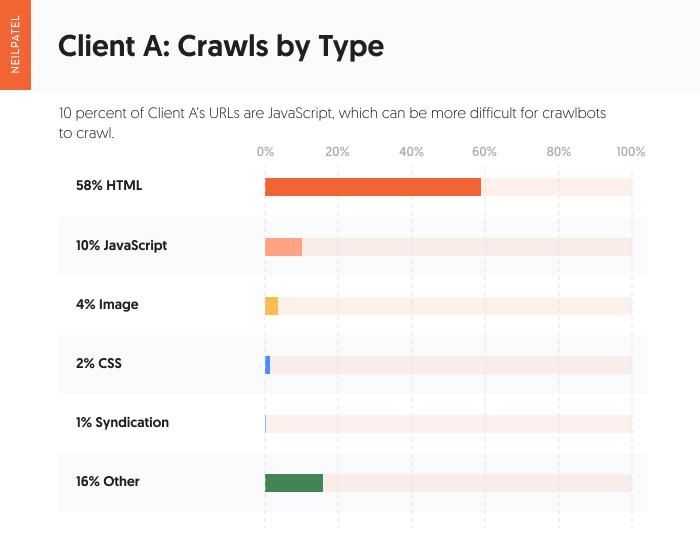
A big quantity (58 %) of the location recordsdata for Consumer A are HTML. You’ll discover that JavaScript is clearly current, too, with 10 % of requests being answered by a JavaScript file sort.
JavaScript could make your website extra interactive for human customers, however it may be tougher for crawlbots to navigate. This may increasingly hinder efficiency on SERPs which is why JavaScript search engine optimisation finest practices should be adopted for optimum efficiency and expertise.
By Function
Lastly, let’s take a look at the requests by goal.
In Consumer A’s case, 13 % of the crawl goal is discovery with the remaining 87 % being labeled refresh.
Consumer B
Subsequent up is a pure artesian water model based mostly in California, United States.
By Response
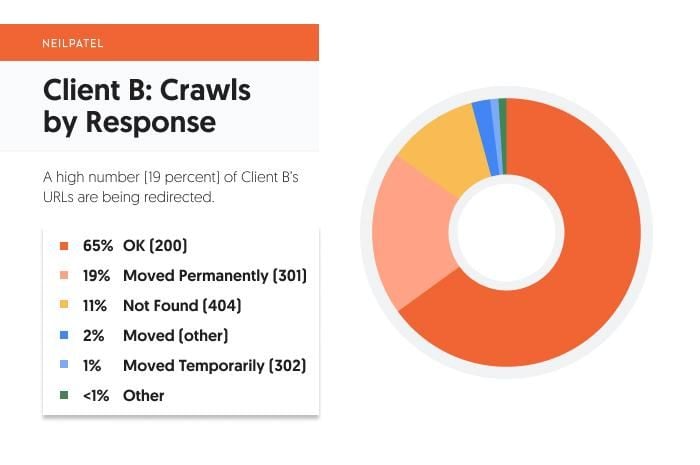
Just like Consumer A, the bulk (65 %) of Consumer B’s response sort are 200 standing OK URLs. Nonetheless, the distinction between the OK standing URLs and redirects is just not as giant as one would need it to be.
Of the redirects, 19 % are 301 (everlasting) and one % are 302 (non permanent). That’s nonetheless a wholesome steadiness between the 2, although 20 % of URL responses being redirects is sort of excessive.
So, what can Consumer B do to make sure the redirects aren’t negatively impacting crawl indexing or consumer expertise?
One factor they’ll do is guarantee their 301 redirects don’t embody any redirect chains.
A redirect chain is simply what it feels like—a number of redirects that happen between the preliminary URL and the ultimate vacation spot URL.
The best expertise is only one redirect, from Web page A (supply URL) to Web page B (goal URL). Nonetheless, typically you will get redirect chains that imply Web page A goes to Web page B which works to Web page C, and so forth. This may increasingly confuse the customer and gradual web page load occasions.
As well as, it will probably confuse crawlbots and delay the crawling and indexing of URLs in your web site.
So, what’s the reason for redirect chains?
It’s most frequently an oversight. That’s, you redirect to a web page that already has a redirect in place. Nonetheless, it can be induced throughout web site migrations. See the graphic under for an instance:

By File Sort
Now let’s think about the crawl by file sort.
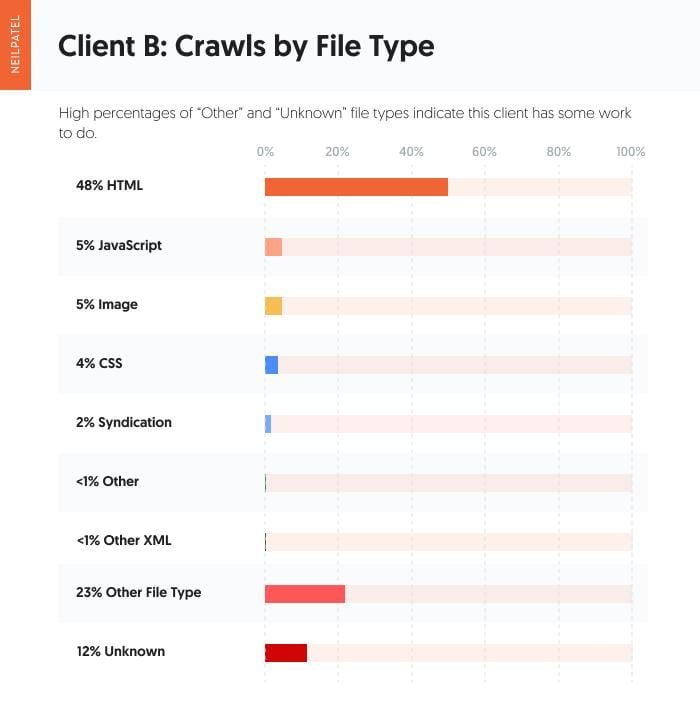
Consumer B has fairly a excessive share of “Different” file varieties at 23 %. There’s nothing inherently improper with the “Different” file sort assuming you understand what these file varieties are. The “Different” file sort simply means something outdoors of the opposite outlined file varieties, and it will probably even embody redirects.
Nonetheless, mixed with the 12 % “Unknown (failed requests),” it’s one thing for the shopper to dig into and resolve.
By Function
The breakdown of goal for Consumer B is 90 % refresh and 10 % discovery.
As talked about above, there is no such thing as a proper and improper breakdown right here. Nonetheless, with such a excessive refresh crawl fee, it will be a good suggestion to make sure that your pages are optimized for the following crawl. How? First is to scrub up 404 errors. Arrange redirects, ideally 301s.
When doing so, make certain the 301 redirects will not be chained. If present redirects exist, simply make sure you break that relationship earlier than creating the brand new 301 for that URL.
Consumer C
The third and last shopper we analyzed is a meals reward retailer based mostly in Illinois, United States.
By Response
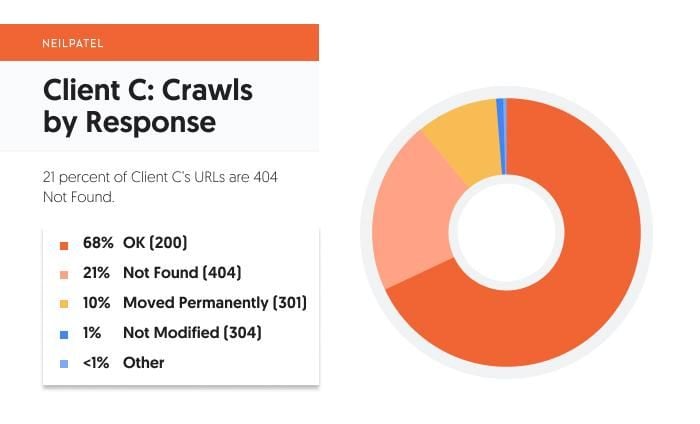
Just like Purchasers A and B, the bulk (68 %) of Consumer C’s response varieties are 200 Standing OK URLs.
The place we veer into new territory is with Consumer C’s 404 Not Discovered URLs, that are a whopping 21 % of their whole response varieties to crawlbots.
Why would possibly this be the case?
The most probably wrongdoer is easy oversight.
When a web page is moved or deleted, as so occurs every now and then, a 301 or 302 redirect should be set as much as direct visitors elsewhere. These moved or deleted pages are likely to occur on a smaller scale, like when a product is not bought by an organization. As an e-commerce model, studying to take care of out-of-stock or discontinued merchandise requires tactical precision and alignment between gross sales and advertising.
Nonetheless, an internet site area switch may cause this to occur on a a lot bigger scale.
Not all area transfers happen inside a one-to-one framework. By that, I imply that your new website’s construction could not match your outdated website’s construction precisely.
Let’s say your outdated web site had class pages as a part of its construction, however the brand new website doesn’t. Though there’s not a one-to-one URL redirect, you continue to have to redirect these URLs. Or else, you get a lot of 404 errors:
Even inside a one-to-one framework switch, although, the redirects should be arrange by the web site proprietor.
Talking of redirects, Consumer C does have some everlasting redirects established. They make up 10 % of the location’s response varieties. As for non permanent redirects, these make up lower than 1 % of the response varieties.
By File Sort
Leaping into the file sort breakdown, Consumer C has a better share of JavaScript file varieties than the opposite two shoppers. The JavaScript file sort is 13 % of requests. “HTML” (43 %) and “Different” (12 %) are the opposite main file varieties being crawled.
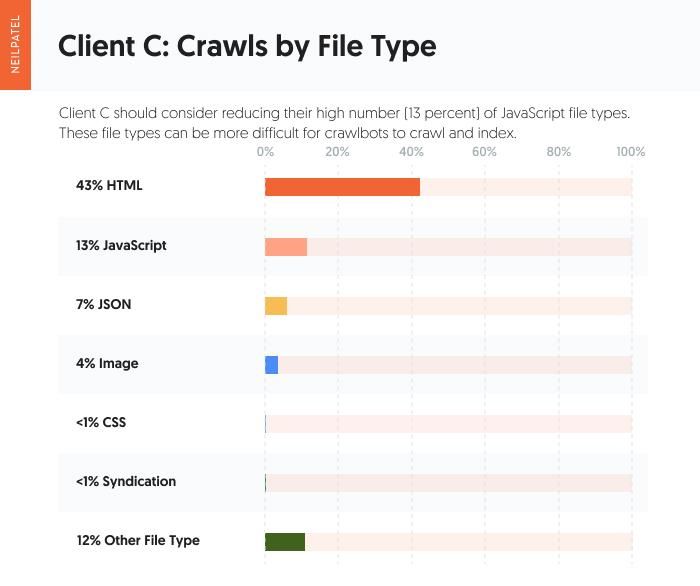
A reminder right here that JavaScript file varieties may be tougher for crawlbots to crawl and index. So in advising Consumer C, I might advocate they examine these JavaScript file varieties and hold solely what’s required.
By Function
Final however not least, let’s take a look at the By Function breakdown for Consumer C.
Consumer C has an 83 % refresh fee which is the bottom of the three shoppers, although not outdoors the “norm.” This merely signifies that Consumer C is at present publishing extra new content material than Purchasers A and B.
Once more, it wouldn’t be a nasty thought for Consumer C to guage their redirects (particularly searching for redirect chains). Within the case of Consumer C, they need to additionally focus closely on correcting these 404 errors.
The Common Crawl Responses, File Varieties, and Functions
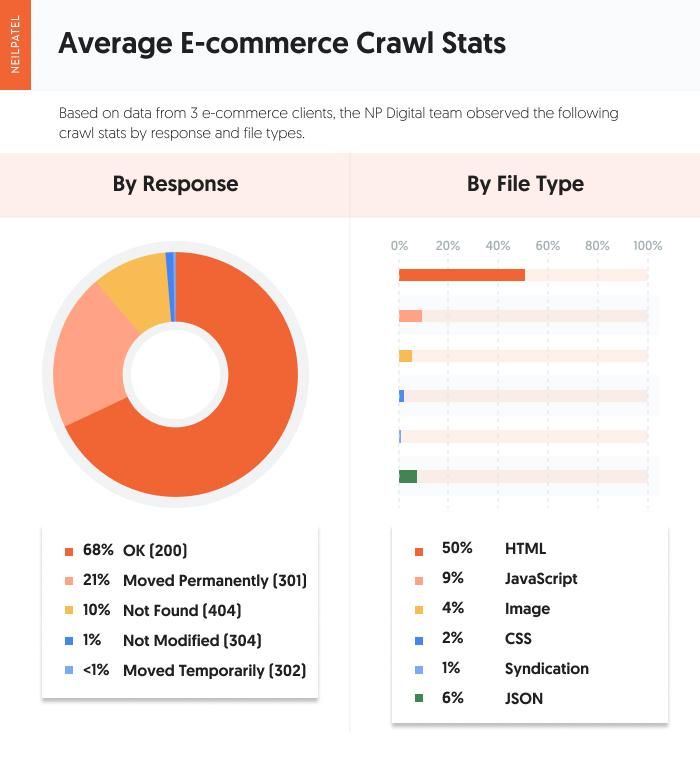
Now that we’ve analyzed every shopper, let’s check out the averages throughout the board:
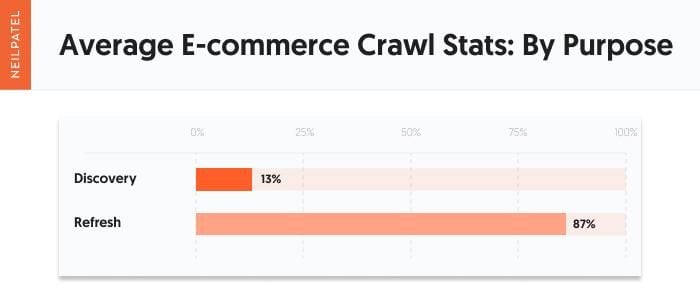
And the e-commerce crawl stats averages by goal:
Wanting on the common crawl stats, OK (200) standing URLs are the core response sort. 301 redirects are subsequent, and that’s not stunning in e-commerce, the place merchandise and collections are sometimes phasing out and in.
One “shock” right here is that the typical fee of HTML file varieties is 50 %, which is decrease than our workforce anticipated. Nonetheless, its edge over JavaScript is to be anticipated, contemplating the problems that crawlbots have with JavaScript recordsdata.
Insights From the Crawl Response of These E-Commerce Corporations
We’ve delved into three e-commerce web sites and found how Google is crawling their websites and what they’re discovering.
So, how will you apply these learnings to your individual web site?
- Minimize down on 404 responses. It is best to first decide whether or not it’s a real 404, or a smooth 404. You possibly can then apply the proper repair. If it’s a true 404 error, you need to create the suitable redirect. If it’s a “smooth” 404, you’ll be able to work to enhance the content material and reindex the URL.
- Create good redirects. Should you should create a redirect, it’s vital that you just select the proper one for the state of affairs (non permanent or everlasting) and that you just guarantee there is no such thing as a redirect chaining.
- Consider the need of JavaScript file varieties. Crawlbots could have bother crawling and indexing JavaScript file varieties, so revert to an HTML file sort when doable. Should you should use JavaScript, then enabling dynamic rendering will assist to cut back crawl load considerably.
- Use crawl goal to gut-check your website’s indexing actions. Should you not too long ago made adjustments (e.g., added new pages, up to date current pages) however the corresponding goal share hasn’t budged, then make certain the URLs have been added to the sitemap. You may as well improve your crawl fee to have Google index your URL extra shortly.
With the above efforts mixed, you’ll see a marked enchancment in your crawl stats.
FAQs
What are crawl stats?
Crawl stats are info that lets you perceive how crawlbots crawl your web site. These stats embody the variety of requests grouped by response sort, file sort, and crawl goal. Utilizing the GSC Crawl Stats report, you can even see an inventory of your crawled URLs to higher perceive how and when website requests occurred.
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@sort”: “FAQPage”,
“mainEntity”: [
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “What are crawl stats?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “
Crawl stats are information that helps you to understand how crawlbots crawl your website. These stats include the number of requests grouped by response type, file type, and crawl purpose. Using the GSC Crawl Stats report, you can also see a list of your crawled URLs to better understand how and when site requests occurred.
”
}
}
]
}
Conclusion
In case your URLs aren’t being correctly crawled and listed, then your hopes of rating are nil. This implies any search engine optimisation enhancements you make to your non-crawled, non-indexed internet pages are for nothing.
Happily, you’ll be able to see the place every URL in your web site stands with GSC’s Crawl Stats report.
With this crawl information in hand, you’ll be able to tackle widespread points that could be hindering crawlbot actions. You possibly can even monitor this efficiency month-over-month to get a full image of how your crawl stat enhancements are serving to.
Do you’ve got questions on crawl stats or Google Search Console’s Crawl Stats report? Drop them within the feedback under.


